As New York City continues to grow, electricity demand is rising, placing increased pressure on the power grid—especially during peak usage. Traditionally, utilities would respond by building new substations, but in dense urban neighborhoods, limited space, lengthy timelines, and disruptive construction can present significant hurdles. To tackle these challenges more effectively, Con Edison launched the Brooklyn-Queens Demand Management Program, which focuses on installing battery storage systems directly in neighborhoods with the highest energy demand. These systems can feed power back into the grid, helping to alleviate bottlenecks in the existing infrastructure and improve energy availability in the area.
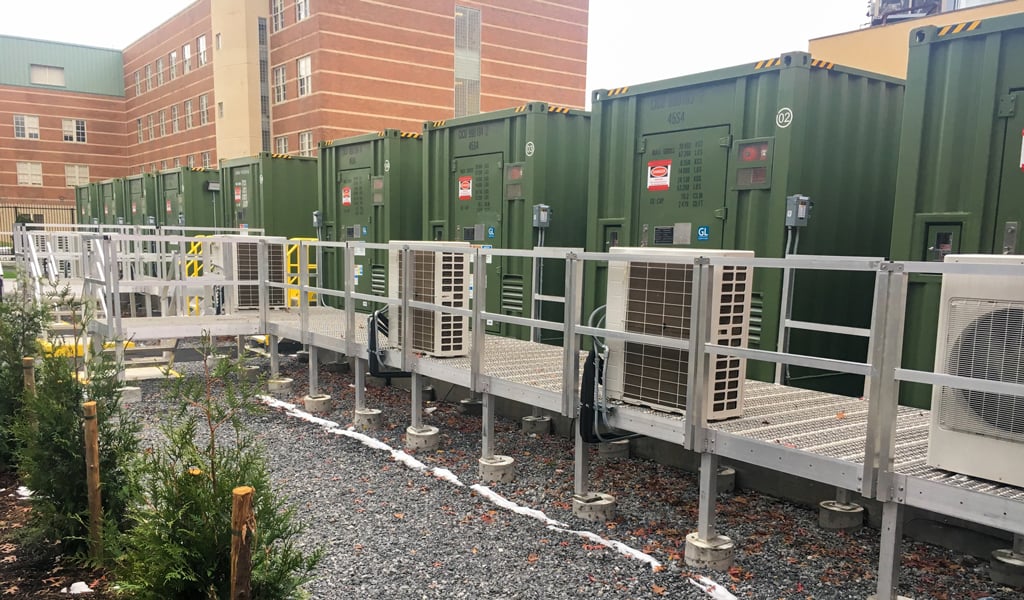
As part of this effort, RES Americas engaged VHB to provide site planning, local permitting, and environmental services in support of the installation of a Distributed Energy Storage System (DESS) in the Ozone Park neighborhood of Queens. The system includes eight battery containers, a power conditioning system container, and two transformers that manage primary and auxiliary power capable of powering approximately 1,000 homes during peak demand.
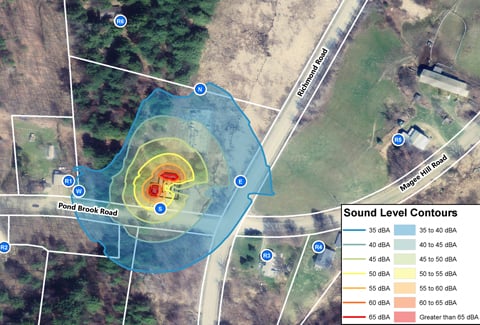
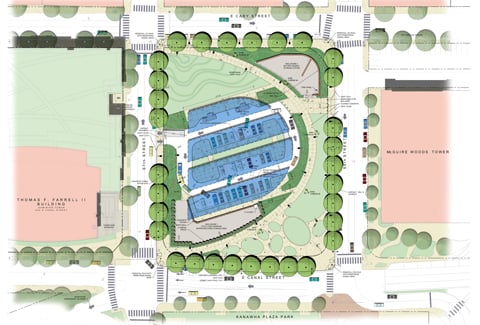
To fit the equipment into a tight urban footprint, VHB’s site plan addressed the proposed geometric layout, dimensional requirements, and required buffers. The team conducted a noise study and collaborated closely with the NYC Department of Buildings and Fire Department to expedite permitting and keep the project on track.
By making clean energy available where and when it’s needed most, this project powers a cleaner, smarter, and more resilient electric grid—fueling New York City’s neighborhoods today and into the future.